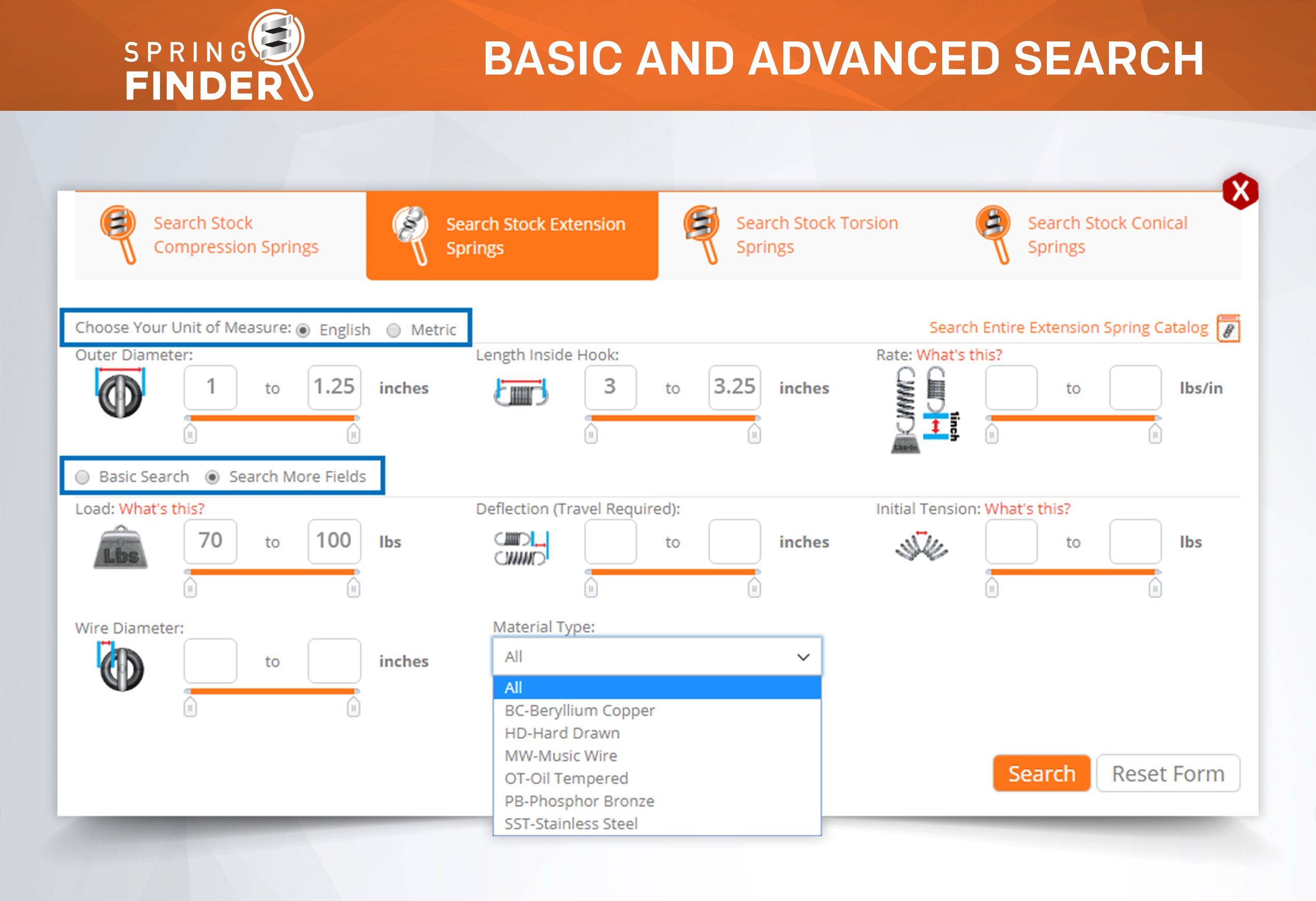
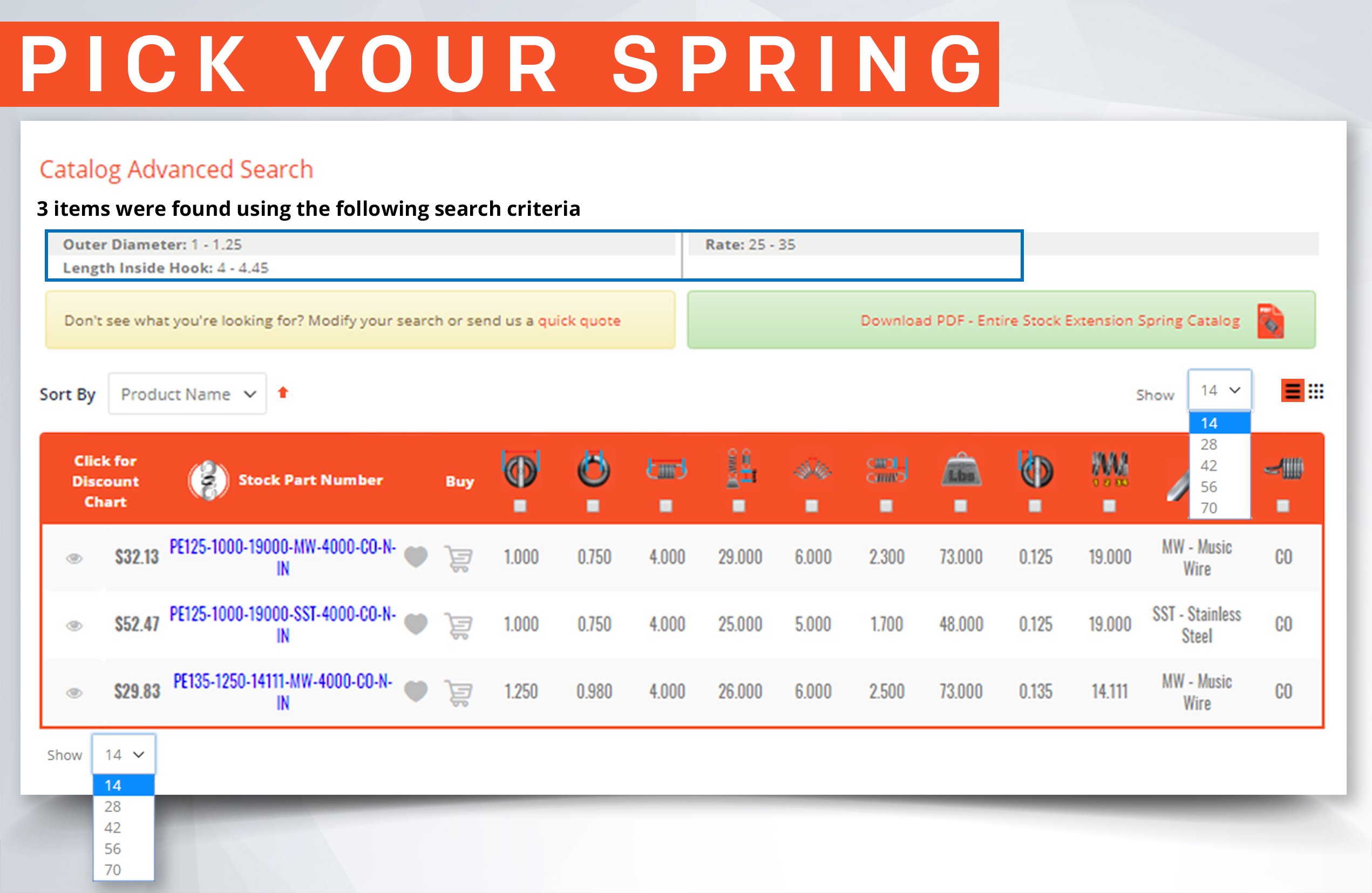
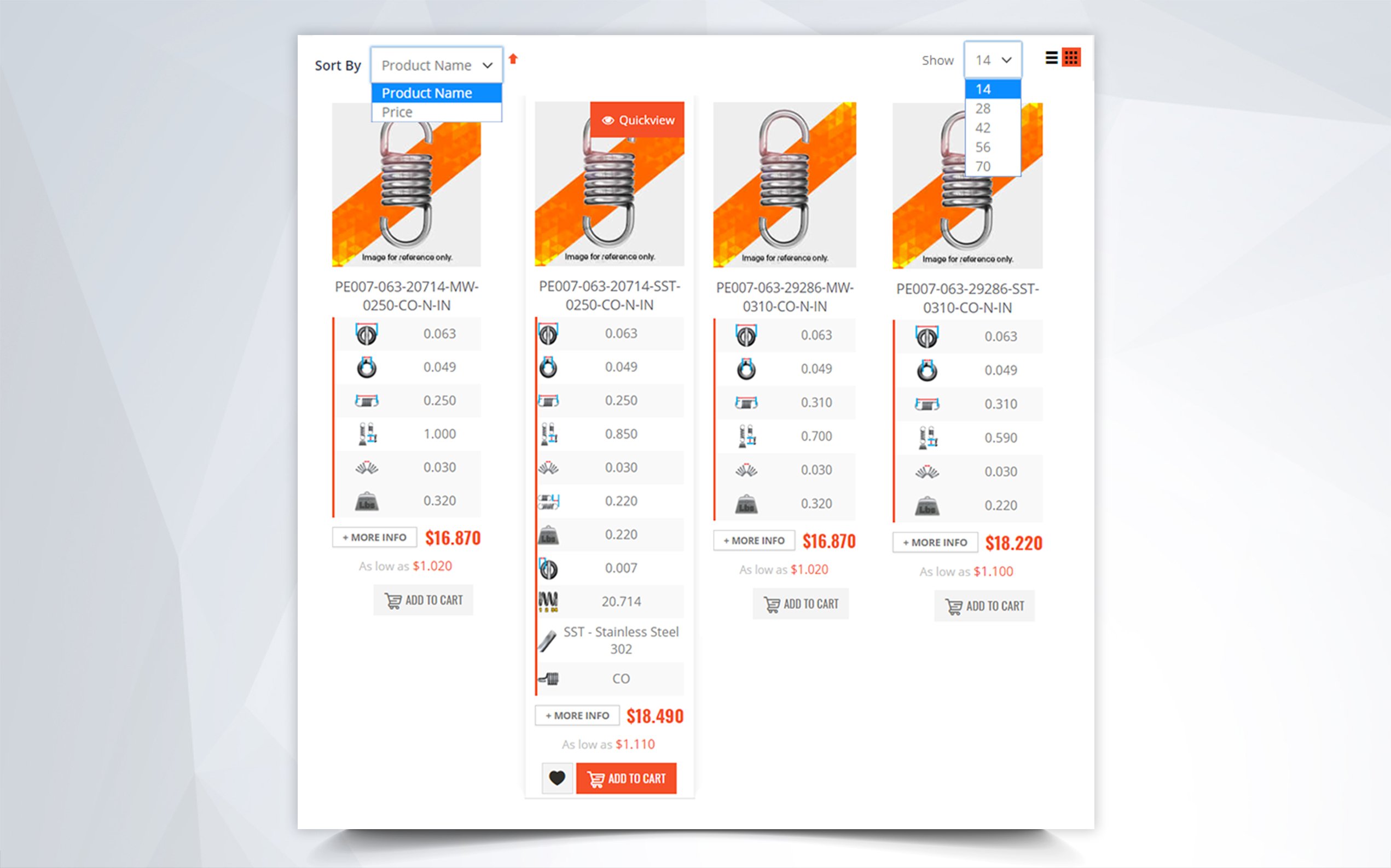
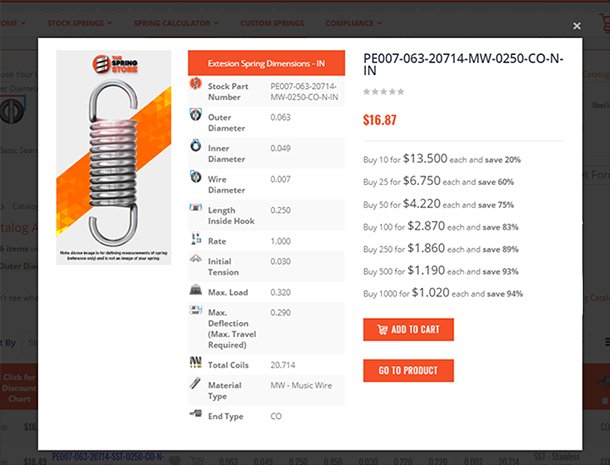
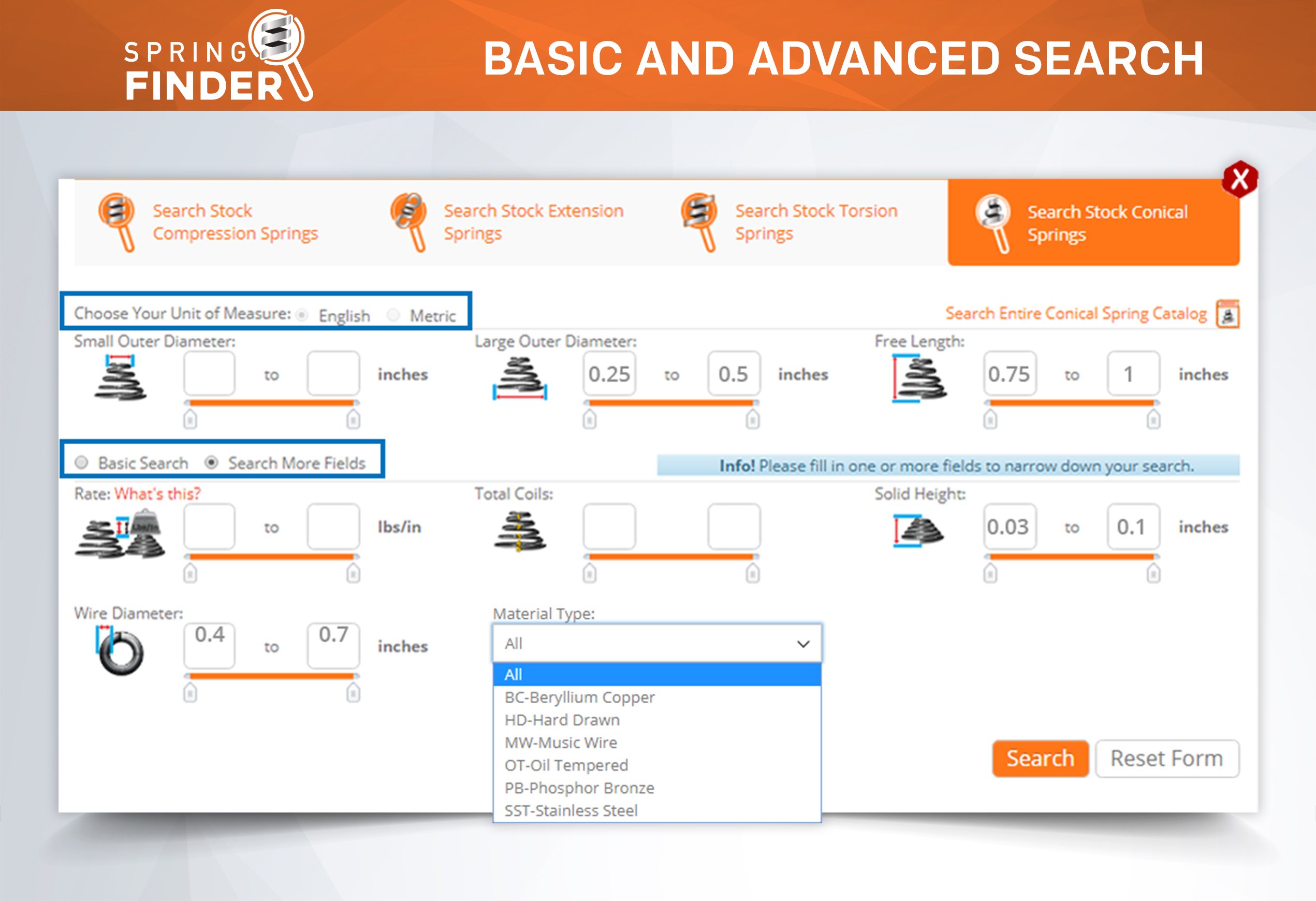
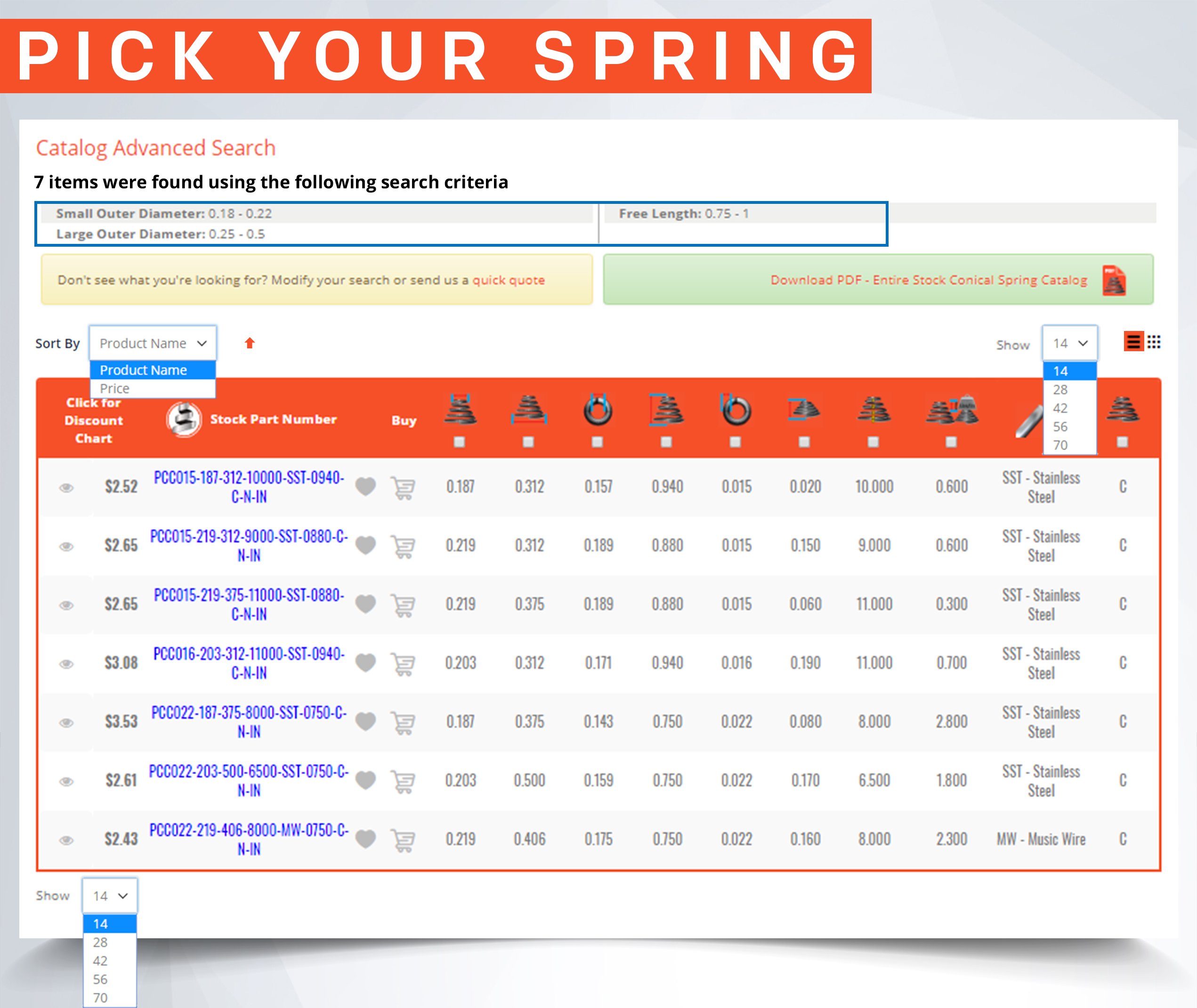
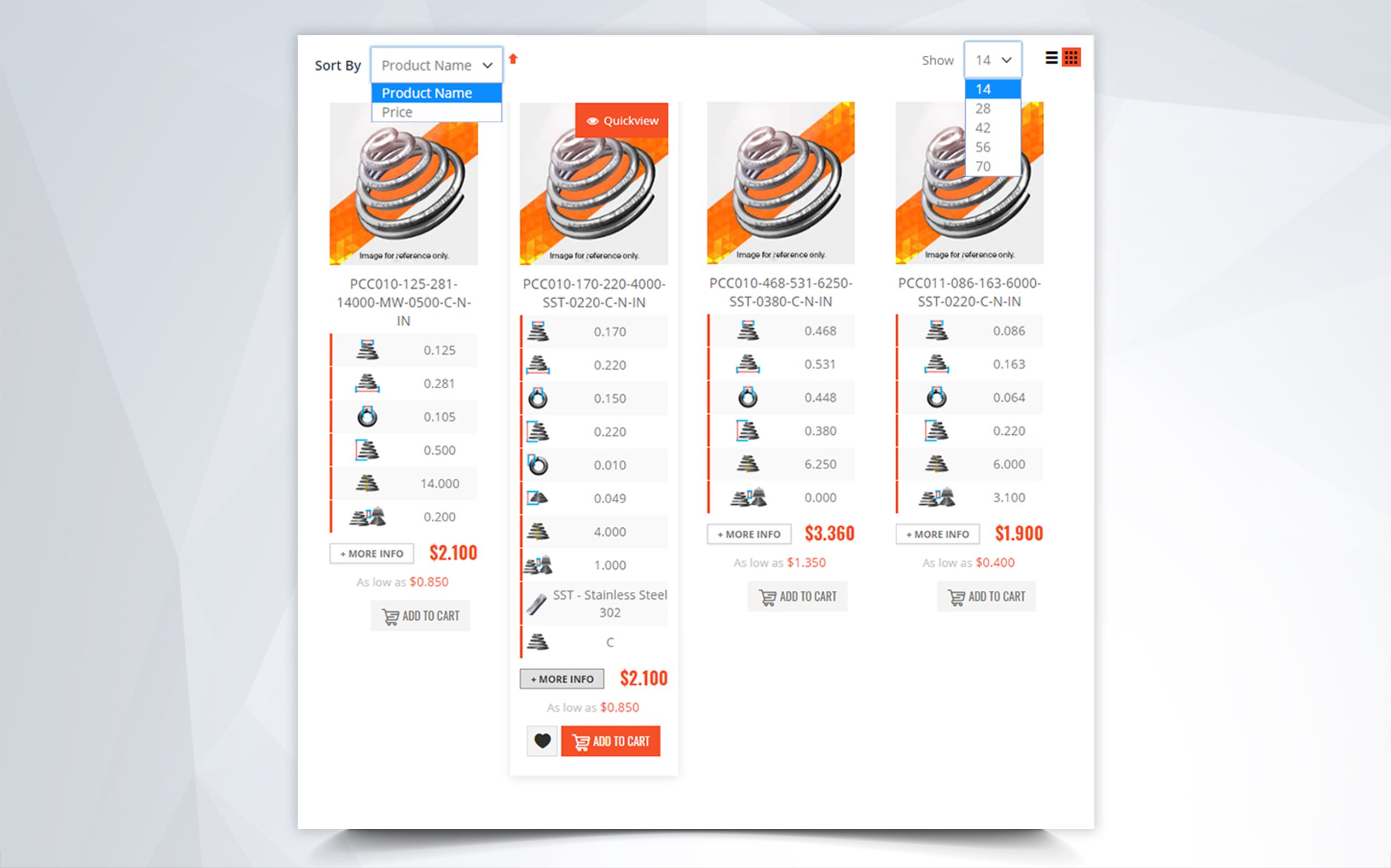
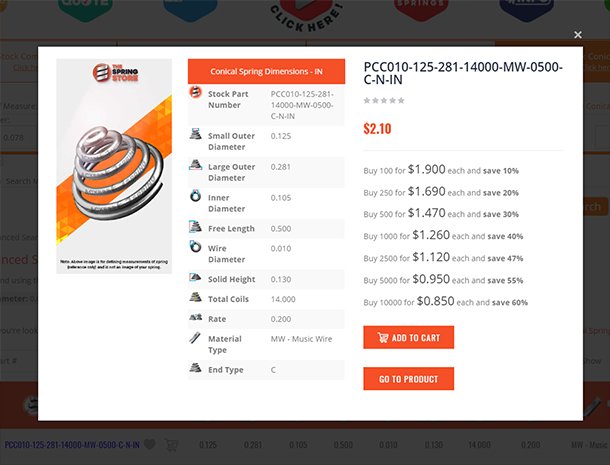
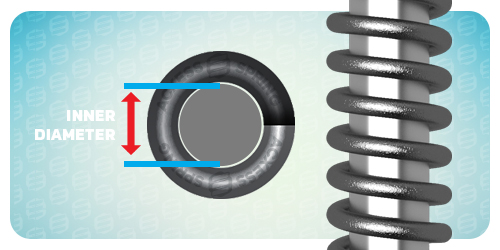
Inner Diameter When Selecting a Stock Compression Spring
Inner Diameter Definition: The width of a coil spring measured from the inside. The formula to calculate inner diameter is outer diameter minus two wire diameters.
D inner= D outer–2d
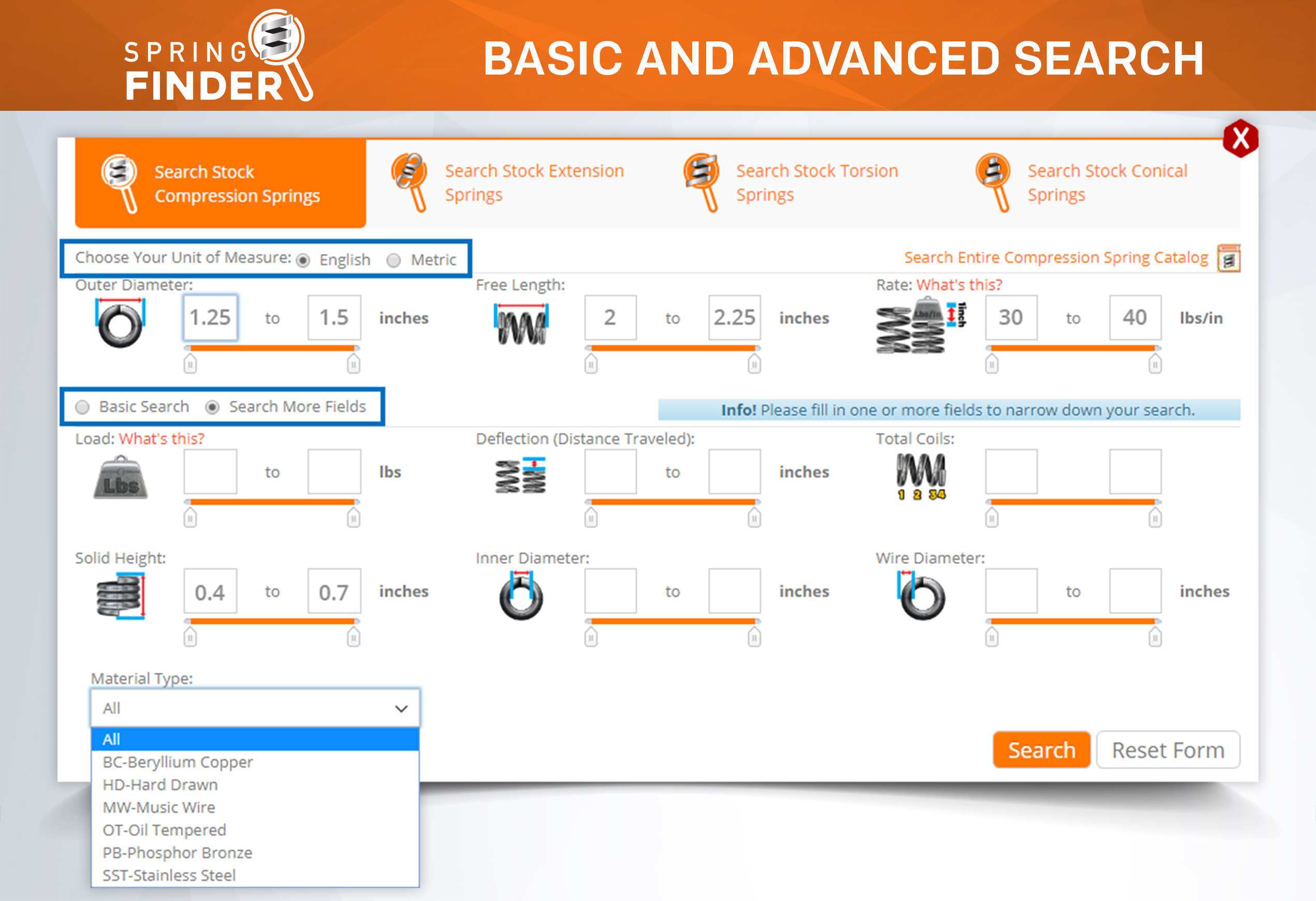
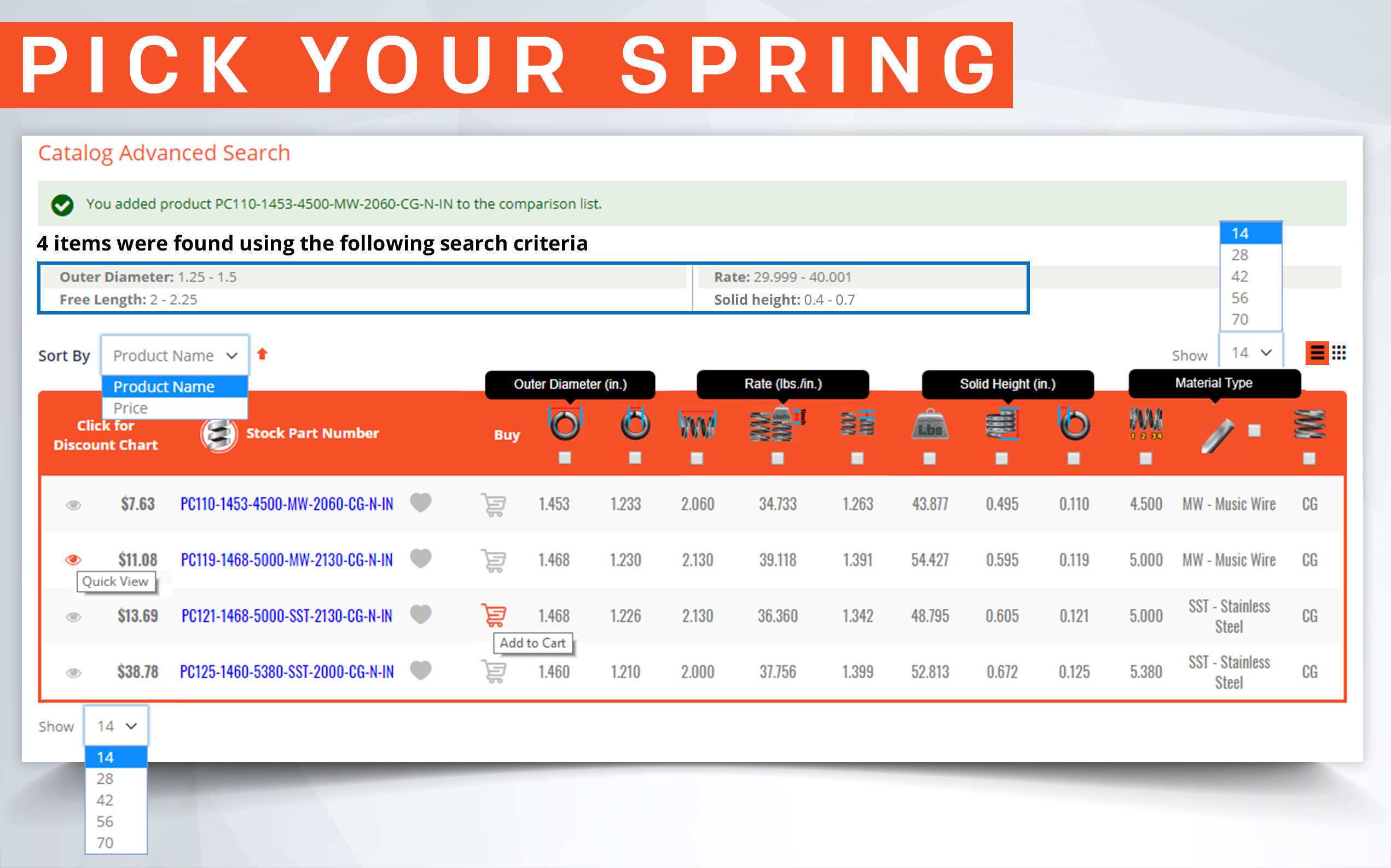
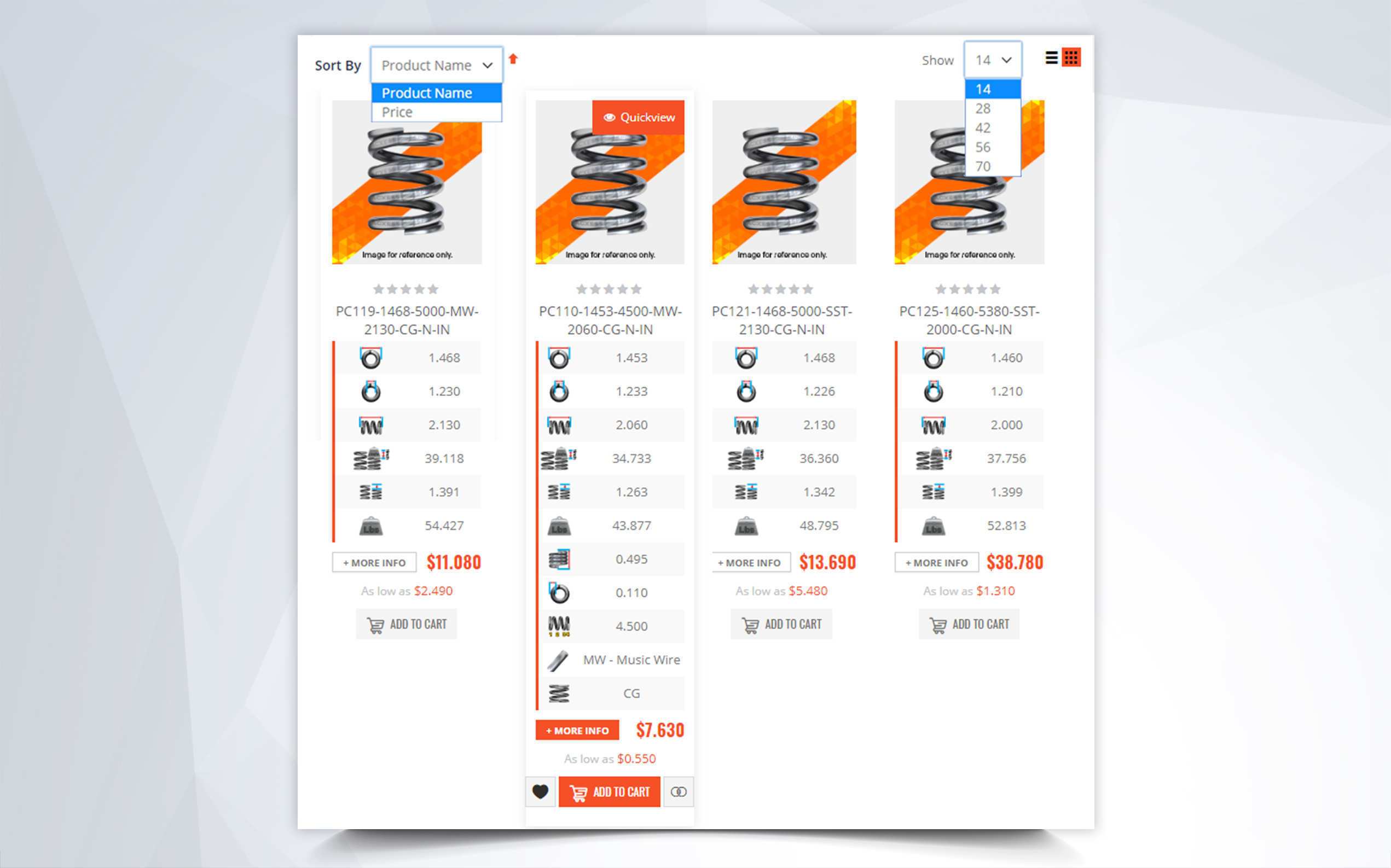
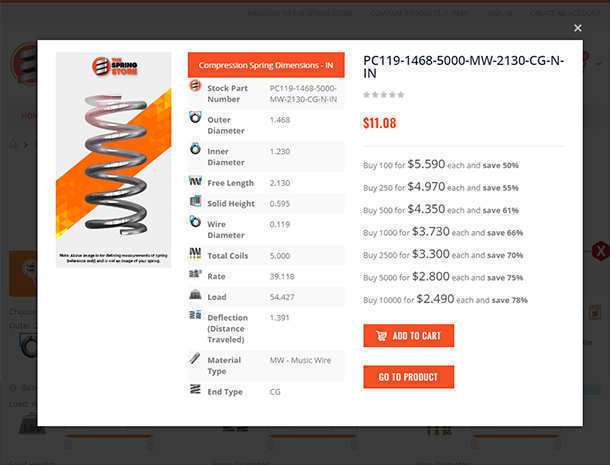
There are many parts and dimensions that you can look at and use to help determine how to buy the ideal stock compression spring. However, we have noticed that inner diameter is sometimes a neglected dimension and it can actually be a key thing to look at depending on where you are placing your metal spring. The following information can help you better determine whether a stock compression spring will work within the space in which you want to place it.
Compression Spring Inner Diameter is an Important Measurement
Some stock compression springs are used over a shaft or mandrel to give the spring stability. This makes it important to have the size of your shaft or mandrel so that you can ensure that the inner diameter of your spring is the perfect size to fit over it. What is the perfect size? The perfect size would mean that the inner diameter of your spring is big enough to avoid any friction during deflection, yet small enough to be stable when compressed. This means that the inner diameter of the spring must allow for 8-10% clearance over a shaft. So if the shaft is 1 inch in diameter you need a spring that at the very least has an inner diameter of 1.1
If a compression spring’s slenderness ratio is too high, the spring will tend to wobble and it will be necessary to place the spring over a shaft or in a tube to prevent it from bending or buckling. Keep in mind that a compression spring’s inner diameter expands during deflection. Although it is very minimal, you want to keep this in mind to make sure it won’t expand past the tolerances that space allows. The inner diameter also plays a role in regards to the spring index, which is a determining factor for the strength and structure of the spring.
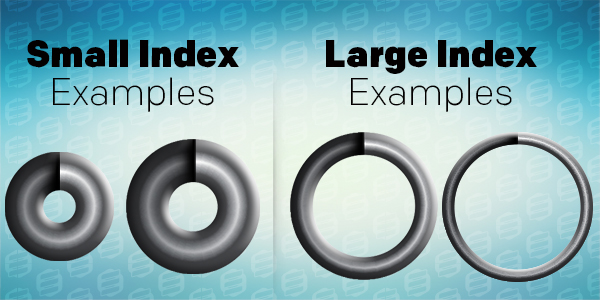
Spring Index
Spring index helps you figure out how tight or loose your compression spring’s coils are. The spring index is basically the proportion bbetween the mean diameter of a spring and the wire diameter of a spring. Calculating the proportional ratio between the coil’s wire diameter and inner diameter/outer diameter will determine the strength of the spring, how stressed it may be, and its manufacturability.
The smaller the spring index, the thicker and stronger a spring tends to be, and it usually means it has a smaller inner diameter in proportion to its wire size. The larger the spring index, the looser and larger the inner diameter tends to be. If the spring index is too small or too large, it may be hard to find a similar stock spring, or it will tend to be at a higher price due to the high difficulty level of manufacturability.
Formula For Calculating Spring Index
Index = Mean Diameter (D) / Wire Diameter (d) Mean Diameter (D) = Outer Diameter (OD) - Wire Diameter (d)Spring Index Calculation Example
A spring index ranging between 6-12 is usually a spring that is within a good manufacturing range. A spring index that is between a 13-15 means your spring is just above good but not quite in the difficult range. Anything higher than 15, or lower than 5 usually means it will be quite difficult to manufacture and the price will tend to reflect that.